
Introducción:
La amebiasis extraintestinal es una infección causada por el parásito Entamoeba histolytica. Este parásito se encuentra comúnmente en los intestinos de las personas infectadas, pero también puede diseminarse a otras partes del cuerpo, como el hígado, el bazo, el pulmón, el cerebro y la piel.
- Amebiasis extraintestinal
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Infección por ameba
- Infección por protozoos
- Hígado
- Bazo
- Pulmón
- Cerebro
- Piel
Cuerpo:
¿Cómo se transmite la amebiasis extraintestinal?
La amebiasis extraintestinal se transmite por la ingestión de quistes de Entamoeba histolytica. Estos quistes pueden encontrarse en el agua o los alimentos contaminados con materia fecal de personas infectadas.
¿Cuáles son los síntomas de la amebiasis extraintestinal?
Los síntomas de la amebiasis extraintestinal varían según la parte del cuerpo afectada.
- Infección hepática: Los síntomas de la infección hepática por ameba incluyen fiebre, dolor abdominal, náuseas, vómitos y fatiga. En casos graves, la infección puede provocar absceso hepático.
- Infección esplénica: Los síntomas de la infección esplénica por ameba son similares a los de la infección hepática.
- Infección pulmonar: Los síntomas de la infección pulmonar por ameba incluyen tos, fiebre, dificultad para respirar y dolor en el pecho.
- Infección cerebral: Los síntomas de la infección cerebral por ameba incluyen dolor de cabeza, fiebre, convulsiones y coma.
- Infección cutánea: Los síntomas de la infección cutánea por ameba incluyen úlceras en la piel.
¿Cómo se diagnostica la amebiasis extraintestinal?
El diagnóstico de la amebiasis extraintestinal se basa en los síntomas del paciente y en los resultados de las pruebas de laboratorio.
- Pruebas de sangre: Las pruebas de sangre pueden detectar anticuerpos contra el parásito Entamoeba histolytica.
- Pruebas de imagen: Las pruebas de imagen, como la tomografía computarizada (TC) y la resonancia magnética (RM), pueden ayudar a identificar la infección.
- Biopsia: En algunos casos, puede ser necesario realizar una biopsia para confirmar el diagnóstico.
¿Cómo se trata la amebiasis extraintestinal?
El tratamiento de la amebiasis extraintestinal se basa en el tipo y la gravedad de la infección.
- Infección hepática: El tratamiento estándar para la infección hepática por ameba es el uso de antibióticos, como el metronidazol o el tinidazol.
- Infección esplénica: El tratamiento para la infección esplénica por ameba es el mismo que para la infección hepática.
- Infección pulmonar: El tratamiento para la infección pulmonar por ameba es el mismo que para la infección hepática.
- Infección cerebral: El tratamiento para la infección cerebral por ameba es complejo y puede requerir el uso de antibióticos, medicamentos antiinflamatorios y cirugía.
- Infección cutánea: El tratamiento para la infección cutánea por ameba es el mismo que para la infección hepática.
Prevención:
La mejor manera de prevenir la amebiasis extraintestinal es evitar la exposición a quistes de Entamoeba histolytica. Esto se puede hacer mediante las siguientes medidas:
- Beber agua potable tratada.
- Lavarse las manos con agua y jabón con frecuencia, especialmente después de ir al baño y antes de comer.
- Evitar comer alimentos crudos o poco cocidos.
- Cocinar bien los alimentos a una temperatura interna de al menos 74°C (165°F).
Conclusión:
La amebiasis extraintestinal es una infección grave que puede afectar a diferentes partes del cuerpo. El diagnóstico y el tratamiento tempranos son importantes para prevenir complicaciones.
WebAmebiasis. Es una infección intestinal. Es causada por el parásito microscópico Entamoeba histolytica. Web3. Amebiasis extraintestinal. 1) Absceso hepático amebiano: es la manifestación extraintestinal más frecuente (a consecuencia del paso del parásito hacia el hígado.
AMEBIASIS « PIMS Prevención en Salud

Source: pimssalud.wordpress.com
Absceso hepático amebiano
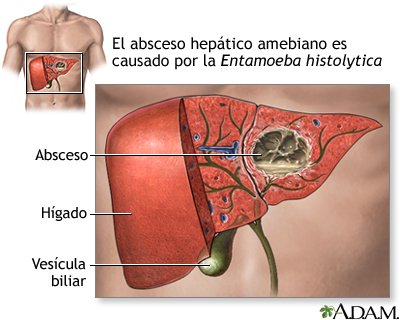
Source: ssl.adam.com
Spanish HIE Multimedia – Absceso hepático amebiano
Source: ssl.adam.com
Que Es Amebiasis Extraintestinal, AMEBAS / ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA ( GENERALIDADES, CICLO DE VIDA, EPIDEMIOLOGIA, PATOGENIA, CLINICA), 50.17 MB, 36:32, 145,944, Jeanpierre Ipanaqué, 2020-03-26T18:51:38.000000Z, 2, AMEBIASIS « PIMS Prevención en Salud, pimssalud.wordpress.com, 405 x 720, jpg, , 3, que-es-amebiasis-extraintestinal
Que Es Amebiasis Extraintestinal. WebLa amebiasis es la infección por Entamoeba histolytica. Se adquiere por transmisión fecal-oral. En general, la infección es asintomática, pero sus síntomas pueden ir desde. WebLa amebiasis es una infección del intestino grueso y algunas veces del hígado y otros órganos, causada por el parásito protozoico unicelular Entamoeba histolytica, una.
Familia de YouTube, ahí les dejo un resumen de la ameba patogena mas frecuente cómo es Entamoeba Histolytica, no olvides suscribirte al
Canal ❤️
AMEBIASIS « PIMS Prevención en Salud
Web3. Amebiasis extraintestinal. 1) Absceso hepático amebiano: es la manifestación extraintestinal más frecuente (a consecuencia del paso del parásito hacia el hígado.
AMEBAS / ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA ( GENERALIDADES, CICLO DE VIDA, EPIDEMIOLOGIA, PATOGENIA, CLINICA)
Source: Youtube.com
Manifestaciones de la Amibiasis

Source: Youtube.com
Difference between intestinal and extraintestinal amoebiasis CDC – DPDx – Amebiasis
Difference between intestinal and extraintestinal amoebiasis Amebiasis – DPDx, Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria (DPDM), DPDx applications, diagnosis of parasitic diseases, diagnostic reference resources, diagnostic quizzes, parasites and parasitic diseases, parasitic diseases, training function, emerging parasitic diseases , global, worldwide, , What is extraintestinal amoebiasis.
What is extraintestinal amoebiasis Amebiasis – Infectious Diseases – Merck Manuals Professional Edition
What is extraintestinal amoebiasis Skin lesions are occasionally observed, especially around the perineum and buttocks in chronic infection, and may also occur in traumatic or operative wounds. Intestinal infection: Microscopic examination, enzyme immunoassay of stool, molecular tests for parasite DNA in stool, and/or serologic testing · Extraintestinal infection: Imaging and serologic testing or a therapeutic trial with an amebicide · Nondysenteric amebiasis may be misdiagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Irritable bowel syndrome is characterized by recurrent abdominal discomfort or pain with at least two of the following characteristics: relation to defecation, association with a change in frequency, read more , regional enteritis Crohn Disease Crohn disease is a chronic transmural inflammatory bowel disease that usually affects the distal ileum and colon but may occur in any part of the gastrointestinal tract. Que es amebiasis intra y extraintestinal.
Que es amebiasis intra y extraintestinal A rare case of extraintestinal amebiasis | BMC Infectious Diseases | Full Text
Que es amebiasis intra y extraintestinal Amoebiasis is caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica, which is a rare infectious disease in developed countries. If the trophozoites enter the blood, it can spread through the body, such as brain, and lungs. Cases of simultaneous infection of multiple organs are extremely rare. Que es amebiasis intestinal y extraintestinal.
.
Que es amebiasis intestinal y extraintestinal Extraintestinal Entamoeba histolytica amebiasis – UpToDate
Que es amebiasis intestinal y extraintestinal It seems to us that you have your JavaScript disabled on your browser. JavaScript is required in order for our site to behave correctly. Please enable JavaScript to use our site Que es amebiasis extraintestinal.
.
Que es amebiasis extraintestinal A rare case of extraintestinal amebiasis – PMC
Que es amebiasis extraintestinal Amoebiasis is caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica, which is a rare infectious disease in developed countries. If the trophozoites enter the blood, it can spread through the body, such as brain, and lungs. Cases of simultaneous infection of multiple , Que es amebiasis intestinal y extraintestinal.
Serodiagnosis of Extraintestinal Amebiasis: Retrospective Evaluation of the Diagnostic Performance of the Bordier® ELISA Kit – PMC
Soluble antigens from an axenic culture of Entamoeba histolytica were used to develop a commercial ELISA kit to quantify anti-E. histolytica antibodies in sera of patients with extraintestinal amebiasis in non-endemic settings. The diagnostic specificity , .
.
Amebiasis Clinical Presentation: History, Physical Examination, Complications
Amebiasis is caused by Entamoeba histolytica (see the image below), a protozoan that is found worldwide (see Etiology). The highest prevalence of amebiasis is in developing countries where barriers between human feces and food and water supplies are inadequate (see Epidemiology). .Extra-intestinal amebiasis: clinical presentation in a non …
37/38 patients with reciprocal titers > or = 512 against Entamoeba histolytica in Denmark over a 5-year period were evaluated retrospectively in order to establish the clinical profile of extra-intestinal amebiasis in a non-endemic area. 24 of these had extra-intestinal amebiasis, all presenting … .
.
CDC – DPDx – Amebiasis – Laboratory Diagnosis
CDC – Home Page without Navigation example description goes here .
Amebiasis: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology
Amebiasis is caused by Entamoeba histolytica (see the image below), a protozoan that is found worldwide (see Etiology). The highest prevalence of amebiasis is in developing countries where barriers between human feces and food and water supplies are inadequate (see Epidemiology). .
Extraintestinal amebiasis. – NCBI
Extraintestinal involvement is a dreaded complication of amebiasis, with a reported mortality rate of 7%-14%. The authors retrospectively studied 188 patients with extraintestinal amebiasis confirmed by means of clinical, surgical, and radiologic criteria over a 45-month period. .
Extra-intestinal amebiasis: clinical presentation in a non-endemic setting – PubMed
37/38 patients with reciprocal titers > or = 512 against Entamoeba histolytica in Denmark over a 5-year period were evaluated retrospectively in order to establish the clinical profile of extra-intestinal amebiasis in a non-endemic area. 24 of these had extra-intestinal amebiasis, all presenting … .
Amebiasis – Knowledge @ AMBOSS
Amebiasis is an infectious disease caused by the anaerobic protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. Transmission usually occurs via the fecal-oral route (e.g., via contaminated drinking water) when traveli, What is chronic amebiasis.
What is chronic amebiasis Amoebiasis : Diagnosis, symptoms, complications …
What is chronic amebiasis Dive into the comprehensive guide on amoebiasis, its causes, symptoms, and prevention. Understand the global impact and the importance of sanitation in combating this gastrointestinal infection. Treatment of extraintestinal amoebiasis.
Treatment of extraintestinal amoebiasis Background. Extraintestinal amoebiasis is more common in countries with lower socioeconomic status. Complication related to amoebiasis is common in pregnant patients with malnutrition and others. Severe cases can be associated with high fatality rates. We would like to report a patient with a presumptive diagnosis of extraintestinal amoebiasis who was on the 6th postpartum day after intrauterine fetal death (IUFD). Case Presentation. The patient was a 31 year-old female who was on 6th postpart
Treatment of extraintestinal amoebiasis Background. Extraintestinal amoebiasis is more common in countries with lower socioeconomic status. Complication related to amoebiasis is common in pregnant patients with malnutrition and others. Severe cases can be associated with high fatality rates. We would like to report a patient with , Difference between intestinal and extraintestinal amoebiasis.